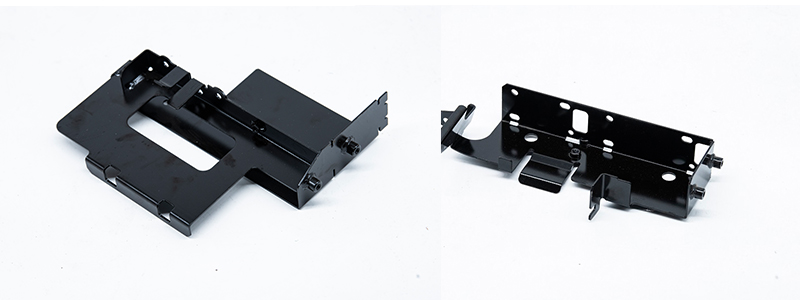
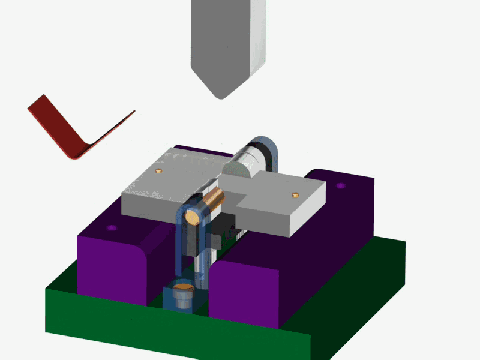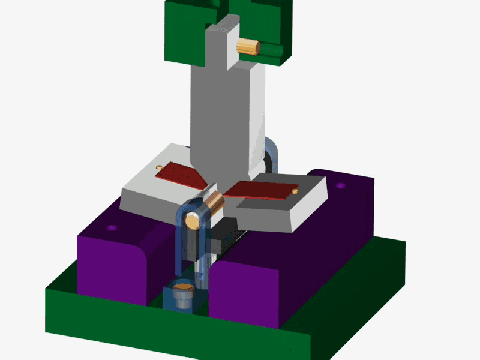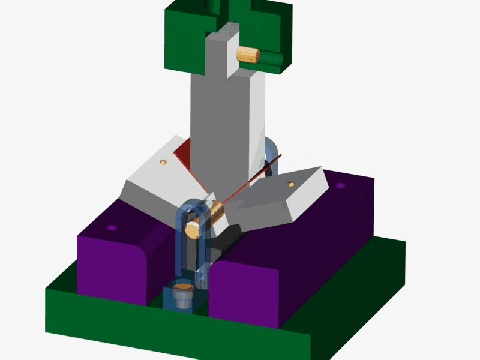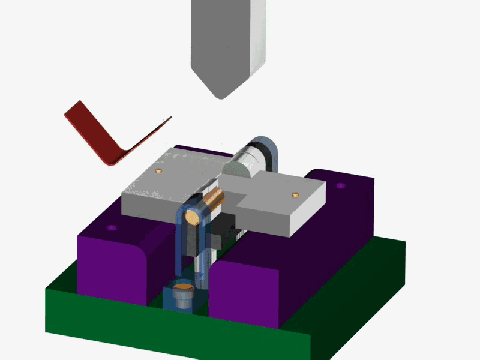
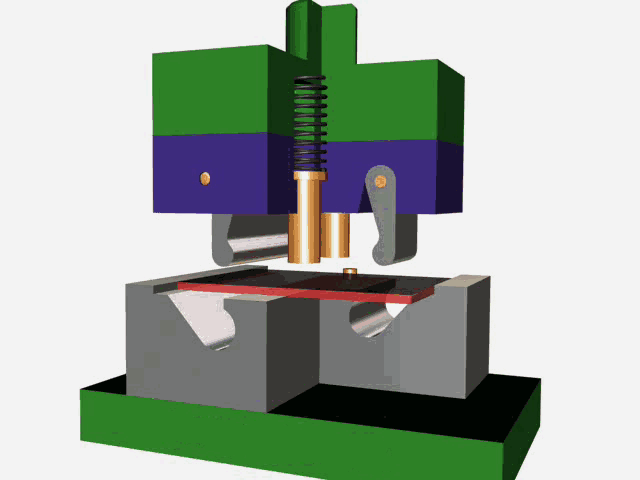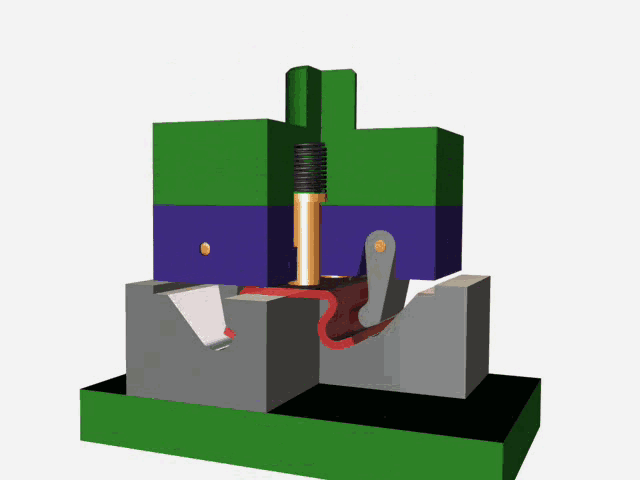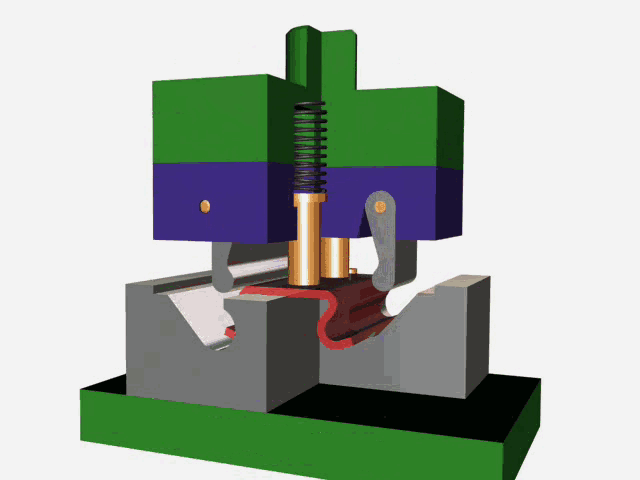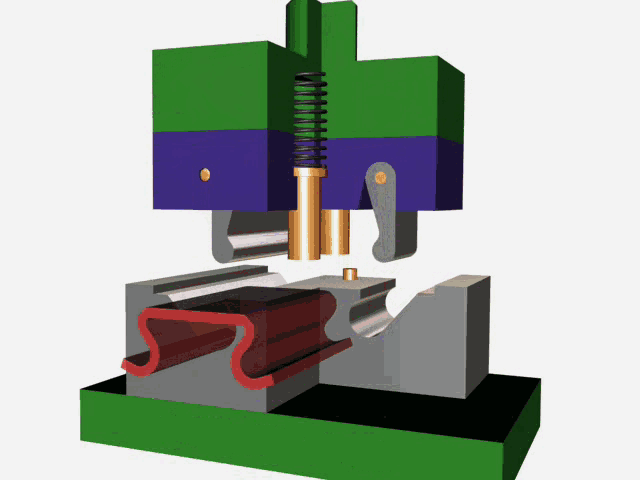
Stamping is a forming processing method that relies on press and die to exert external force on plate, strip, pipe and profile to produce plastic deformation or separation, so as to obtain the required shape and size of the workpiece (stamping parts).
Stamping and forging are both plastic processing (or pressure processing), collectively known as forging. The blanks for stamping are mainly hot and cold rolled steel plates and strips.
Between 60 and 70 percent of the world’s steel is sheet metal, most of which is stamped into finished products. Automobile body, chassis, fuel tank, radiator sheet, boiler drum, container shell, motor, electrical core silicon steel sheet and so on are stamping processing. Instruments, household appliances, bicycles, office machinery, living utensils and other products, there are also a large number of stamping parts.
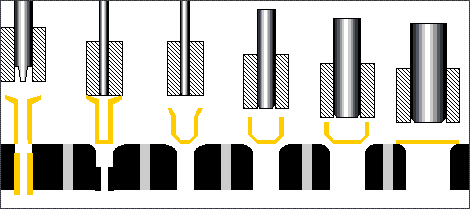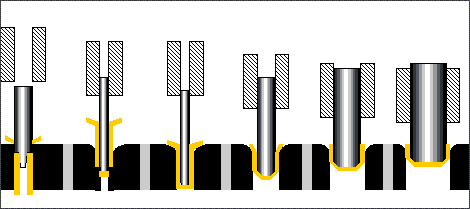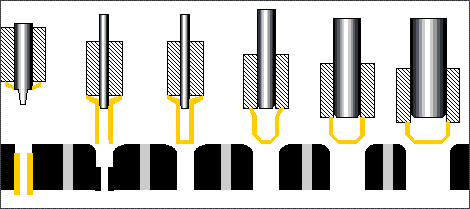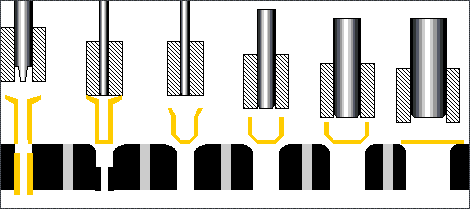
The stamping process can be divided into four basic processes:
Blanking: The process of sheet metal separation (including punching, blanking, trimming, cutting, etc.).
Bending: Stamping process in which sheet material is bent to a certain Angle and shape along a bending line.
Deep drawing: The stamping process in which flat sheet material is transformed into various open hollow parts, or the shape and size of the hollow parts are further changed.
Local forming: A stamping process (including flanging, bulging, leveling and shaping, etc.) in which the shape of a blank or stamping part is changed by local deformation of various properties.
Processing characteristics
1. Stamping processing has high production efficiency, convenient operation, easy to realize mechanization and automation.
2. Stamping quality is stable, good interchangeability, with “identical” characteristics.
3. The strength and stiffness of stamping are high.
4. The cost of stamping parts is low.
Post time: Nov-04-2022